What is environmental sustainability: definition & examples
Imagine holding a scoop of ice cream on a hot day. Eat it right away and you enjoy it. Wait too long, and it melts into a mess. The same goes for our planet. If we don’t prioritise environmental sustainability and take action now, we risk it becoming a place beyond repair. So let’s act now! Let’s make sure our planet doesn’t melt away right before our eyes.
Environmental sustainability isn’t just about tackling climate change, it’s also about addressing other environmental challenges like biodiversity loss, resource depletion and waste. Crucially, all environmental issues are interconnected. That’s why taking a holistic approach is essential to understanding how these issues interlink and creating effective solutions that truly make an impact.
In this blog, we will explain what environmental sustainability is and why it’s so important. This guide will walk you through the environmental sustainability landscape, including the key regulations and initiatives. We’ll also explore the benefits and challenges of companies reducing their environmental impact, where to start, the importance of taking a holistic approach to sustainability and how Root helps companies measure and reduce their environmental impact.
PUBLISHED: 18 September 2024
WRITTEN BY: Charlie Walter
Table of contents
- What is environmental sustainability?
- Why is environmental sustainability important?
- Why are Scope 3 emissions so important?
- The circular economy opportunity
- What are the key environmental sustainability regulations?
- What are the key initiatives accelerating environmental sustainability?
- Companies committed to environmental sustainability
- Benefits of environmental sustainability
- Environmental sustainability challenges
- How to improve environmental sustainability
- The need for a holistic approach to environmental sustainability
- Root’s approach to environmental sustainability
- How we can help
What is environmental sustainability?
The most commonly used definition of environmental sustainability comes from the Brundtland Commission: “meeting the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs.”
But what does this actually mean?
Simply put, environmental sustainability involves protecting ecosystems, conserving resources and creating a healthy world for future generations. It is one of the three key pillars of sustainability, alongside social impact and governance.
Combating climate change is a significant element of environmental sustainability, but it’s not the whole story. Environmental sustainability includes other topics such as waste management, resource depletion and biodiversity loss. Importantly, these issues are interconnected. Companies often focus only one environmental impact, like carbon emissions, while overlooking their products or services’ broader environmental impact. This leads to siloed thinking around environmental issues and unintended consequences. A holistic view is essential to create effective solutions. We explore this in more detail later in the blog.
Why is environmental sustainability important?
To grasp the urgent need to prioritise environmental sustainability, let’s explore the Planetary Boundaries Framework. This framework provides guidance on how to live within Earth’s limits while still meeting human needs.
The Planetary Boundaries theory identifies nine environmental limits, including climate change, biodiversity loss and land-use changes. Crossing these boundaries would result in irreparable damage. Yes, you read that correctly – if we cross these boundaries, we will create irreversible change, no matter what we do after. For example, if we exceed safe carbon emission levels, we risk triggering uncontrollable global warming. Events like Earth Overshoot Day mark the date in the year when our resource use exceeds what Earth can regenerate. This year, Earth Overshoot Day was on August 1st, signalling the urgent need to prioritise environmental sustainability on a global scale.
Human health is also at risk. A World Health Organization study found that 24% of global deaths are linked to avoidable environmental factors like polluted air and contaminated water. Clean air, water and toxin-free ecosystems are vital for healthy living.
Environmental sustainability isn’t just a moral obligation, it’s a smart business move. As environmental challenges worsen, businesses face risks like disrupted supply chains, resource shortages and rising operational costs. A business that understands and reduces its environmental impact will be more resilient and prepared for the future.
The key takeaway? As Greta Thunberg said, we must act now “like our house is on fire.” Rapid, global action is crucial to prevent pushing our planet – and ourselves – past the point of no return.
Are you curious to learn more about why environmental sustainability is so important? Read our blog here.
Image source: Earth Overshoot Day

Why are Scope 3 emissions so important?
Companies measuring and reducing their carbon footprint is a crucial part of environmental sustainability, but what is really important is that companies focus on their Scope 3 emissions. Why? Because up to 90% of a company’s total emissions come from Scope 3. These are indirect emissions from the value chain, covering everything from production to product disposal.
Think of Scope 1 and 2 emissions as the tip of the iceberg. Scope 3 emissions are hidden below the surface but represent the majority of emissions and the most significant opportunity for reduction.
To put it into perspective:
- 98% of Apple’s carbon footprint is Scope 3 emissions
- 98% of Tesla’s carbon emissions are Scope 3
- 95% of Shell’s carbon footprint is Scope 3 emissions
If your company is serious about sustainability, you must measure, set targets and reduce your total carbon footprint, including Scope 3. Ignoring Scope 3 emissions means you’re only scratching the surface of your environmental impact.
Are you interested in learning more about the importance of Scope 3 emissions? Read our Scope 1, 2 and 3 emissions explained blog here.
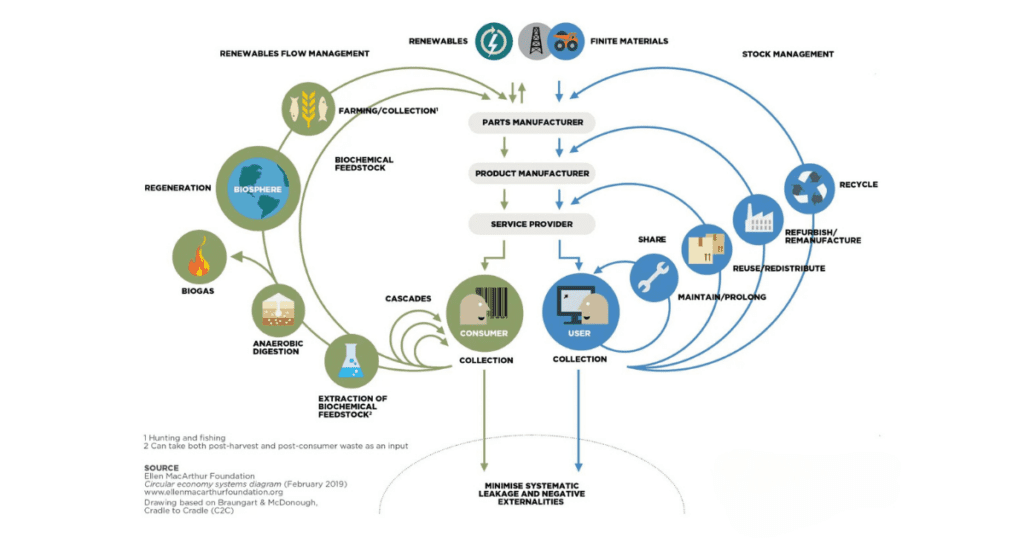
The circular economy opportunity
The circular economy has enormous potential to accelerate environmental sustainability. For example, circular business models could unlock up to $4.5 trillion in market value by 2030. The circular economy presents significant opportunities in industries like fashion, where by 2030, the resale market is expected to double the size of fast fashion.
What is the circular economy?
Most companies still operate in a linear economy – produce, use, dispose. This model isn’t sustainable. The circular economy offers a transformative solution as it tackles the systemic issues of overproduction and overconsumption.
The circular economy focuses on three key principles:
- Eliminate waste and pollution
- Keep products and materials in use
- Regenerate natural systems
Considering the entire life cycle of products and services is a critical component of the circular economy. What this looks like in practice includes initiatives like designing products that can be reused, remanufactured or recycled. You can find examples of circular products and business models on the Ellen MacArthur Foundation website here.
Are you interested to learn more about circularity and its connection to Life Cycle Assessment? Read our blog here.
Image source: The Ellen MacArthur Foundation. The butterfly diagram: visualising the circular economy
What are the key environmental sustainability regulations?
Environmental regulations are becoming more ambitious and changing how companies can operate. The environmental sustainability regulatory landscape is evolving quickly, particularly in Europe. Here are some key regulations driving environmental responsibility across Europe:
- Corporate Sustainability Reporting Directive (CSRD): This pivotal regulation improves transparency by ensuring businesses provide detailed reports on their environmental impact and strategies. This includes companies disclosing their carbon footprint, including the crucial and often overlooked Scope 3 emissions.
- Corporate Sustainability Due Diligence Directive (CSDD): This regulation requires companies to conduct thorough due diligence across their supply chains to uphold high human rights and environmental practices.
- Ecodesign for Sustainable Products Regulation (ESPR): This regulation sets minimum ecodesign requirements and mandates the creation of Digital Products Passports to ensure compliance. Interested to learn more about Digital Product Passports? Read our blog here.
- Green Claims Directive: This regulation combats greenwashing by ensuring businesses can back up their environmental claims with science-based, verifiable data. It’s designed to protect consumers and help them make informed decisions.
Importantly, these regulations are not optional. Non-compliance can result in damage to brand reputation, fines and loss of stakeholder trust. Companies need to start preparing data and changing their sustainability practices to remain compliant and be able to operate in the future.
What are the key initiatives accelerating environmental sustainability?
Several key initiatives are fast gaining momentum and encouraging companies to reduce their environmental impact. Below are some of the most influential ones:
Science-Based Targets Initiative (SBTi)
The Science-Based Targets initiative (SBTi) is a widely respected organisation that supports companies in setting carbon reduction targets and net-zero pathways, which align with the Paris Agreement’s goal of limiting global warming to below 1.5 degrees. SBTi ensures that climate action is based on scientific evidence.
B Corp
B Corp encourages businesses to prioritise sustainability alongside profit. Starting in 2025, the B Corp’s new standards will have minimum requirements that companies must meet, such as large companies developing water stewardship strategies and biodiversity transition plans. The B Corp movement is rapidly gaining momentum, especially in Europe and is an instrumental way for companies to embed sustainability into their business.
Digital Product Passports
Digital Product Passports provide essential transparency throughout a product’s life cycle. These passports help businesses comply with various EU regulations, including the Ecodesign for Sustainable Products Regulation, which mandates the creation of these passports.
The rise of ecodesign
Companies can make more sustainable products by following ecodesign principles. The Ecodesign for Sustainable Products Regulation sets minimum ecodesign requirements, which is accelerating the adoption of ecodesign in Europe.
Companies committed to environmental sustainability
When it comes to environmental leadership, several companies stand out for their ambitious commitments and innovative initiatives:
Patagonia
Patagonia has long been a sustainability icon. The company has ambitious, industry-leading commitments, such as a goal to have waste-free packaging as part of its commitment to eliminating single-use packaging by 2025. One famous initiative is Patagonia’s Worn Wear program, which promotes circularity by encouraging customers to repair and reuse their gear.
IKEA
IKEA aims to be a fully circular business by 2030, making it a trailblazer in circularity. The company has recently launched a second-hand marketplace and is rolling out its Forest Positive strategy to enhance biodiversity and manage forests sustainably.
Ben & Jerry’s
Ben & Jerry’s is pioneering regenerative agriculture in its dairy supply chain, showing how even high-emission industries can embrace sustainability. The company has an ambitious commitment to reducing its Scope 1, 2 and 3 emissions by 40% by 2025, with a target of reaching net zero by 2040.
These companies are not just setting ambitious targets but also creating a blueprint for sustainable business. By doing so, they inspire others to follow suit and help accelerate environmental sustainability in their industries.
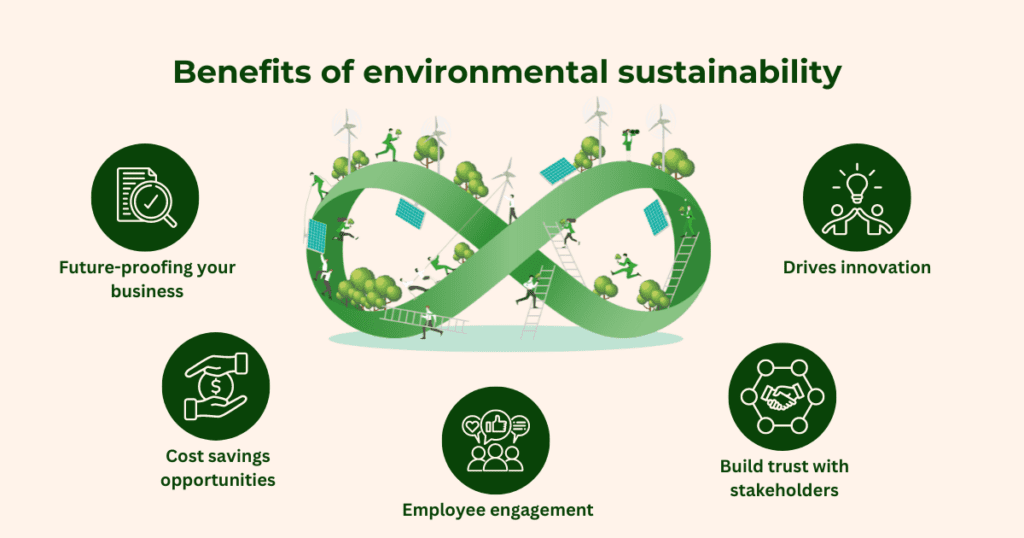
Benefits of environmental sustainability
Reducing your environmental impact offers your company numerous benefits, including:
Future-proofing your business
Focusing on sustainability now helps companies stay ahead of increasingly ambitious environmental regulations and avoid supply chain disruptions. Integrating sustainable practices makes your business more resilient and better equipped to manage future risks.
Cost savings opportunities
Sustainable practices, such as reducing waste and improving energy efficiency, can lower operational costs. The most significant savings lie within the value chain, such as Scope 3 carbon emissions.
Employee engagement
With around 75% of Millennials seeking purpose-driven jobs, setting environmental targets, creating sustainability strategies, and showing progress toward these goals helps attract and retain top talent.
Build trust with stakeholders
Sustainability builds trust with key stakeholders like investors and consumers. Investors increasingly favour companies with robust sustainability strategies, and consumer demand for more sustainable products continues to rise, as seen by over 80% of consumers willing to pay more for eco-friendly options. By prioritising sustainability, businesses can capture market share and strengthen relationships with investors and consumers.
Drives innovation
Understanding your product’s entire life cycle impact unlocks opportunities for innovation. Companies can create new products, services or business models that meet growing consumer demand for sustainable solutions, which helps drive business growth.
The key takeaway? Prioritising environmental sustainability is no longer optional. It’s essential for companies to remain competitive and resilient in a rapidly changing market.
Environmental sustainability challenges
Achieving environmental sustainability presents numerous challenges for companies. Below are some of the most significant hurdles companies face:
Untransparent supply chains
One of the biggest sustainability challenges is managing global supply chains and understanding their environmental impact. When companies have untransparent supply chains, measuring and improving their sustainability performance is difficult.
Are you interested in learning more about supply chain transparency? Read our blog here.
Lack of internal buy-in
Achieving sustainability goals requires internal buy-in, especially from senior leadership. Securing the necessary resources and budget can be challenging without commitment at the top.
High costs of sustainable innovation
Sustainable innovation often requires significant upfront investment in new technologies, materials or processes. This can be a barrier for small and medium-sized enterprises.
Navigating evolving regulations
Keeping up with ever-changing sustainability regulations is time and resource-intensive. However, non-compliance can lead to fines, loss of stakeholder trust and reputational damage. Therefore, staying on top of regulatory changes is a challenge for companies.
Despite these challenges, prioritising environmental sustainability is essential for staying competitive and securing long-term business resilience.
How to improve environmental sustainability
So, where should companies begin when reducing their environmental impact? Below are several key steps to get started:
Focus on supply chain transparency
The majority of a company’s impact lies within its supply chain. You can’t manage what you can’t measure, so improving transparency and gathering data on your supply chain is essential for reducing impact. Building solid relationships with suppliers is also critical for improving the sustainability performance of your supply chain.
Prioritise sustainable product design
Did you know that 80% of a product’s environmental impact is determined at the design stage? That’s why focusing on sustainable product development is crucial. Educate product design teams so they are empowered with the knowledge and tools to choose more sustainable materials and processes. Companies can significantly reduce their overall impact by prioritising improving sustainability at the design stage.
Conduct Life Cycle Assessments for your product portfolio
LCAs for your product portfolio provide comprehensive insights into your product footprints. This data enables informed, data-driven decisions, and the data is the foundation for all sustainability strategies, such as carbon reduction targets.
Build a culture that celebrates sustainability
Sustainability requires stakeholder buy-in, especially from senior leadership. This helps secure the resources needed to drive impact in your business. Involve employees in shaping sustainability strategies and create internal sustainability champions who can lead and inspire teams to take ownership of initiatives.
Be honest in your communication
Sustainability is a journey, so transparency about your sustainability initiatives is critical to building trust with stakeholders. Publish annual impact reports and be open about your progress – even when you face challenges. Being honest about achieving milestones and overcoming obstacles builds credibility and shows a genuine commitment to positive change.
The need for a holistic approach to environmental sustainability
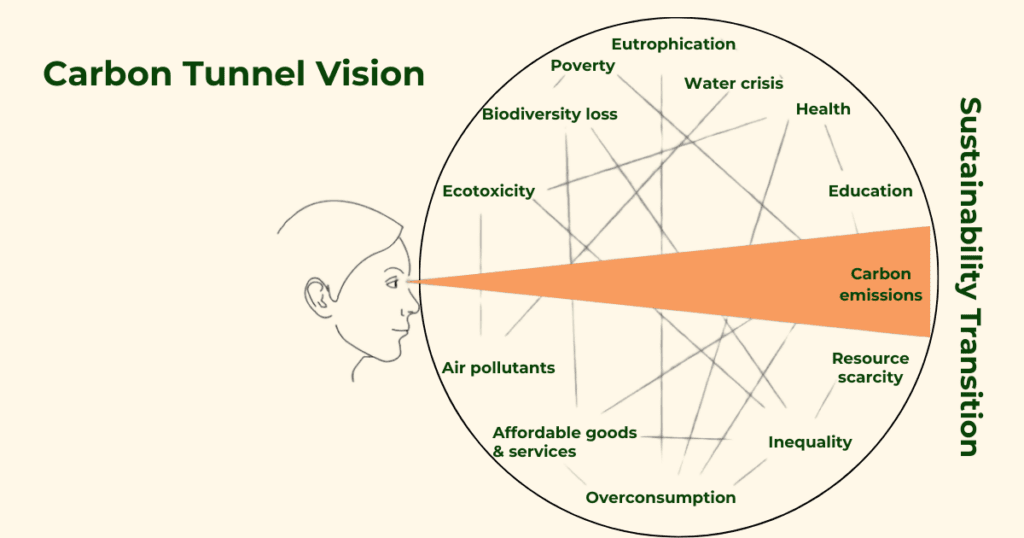
A holistic approach is essential for accurately measuring and reducing a company’s environmental impact. Focusing only on one metric, like carbon emissions, can lead to siloed thinking and unintended consequences. Often, companies are criticised for ‘carbon tunnel vision’, which is when they only focus on carbon emissions of their products without understanding their product’s broader environmental impact, e.g. biodiversity and waste. On the other hand, using product footprints that incorporate a range of environmental metrics allows businesses to make more informed, impactful decisions.
Life Cycle Assessments (LCAs) provide the comprehensive data needed for this approach, offering insights into a product’s environmental footprint throughout its life cycle. By using LCAs, businesses can develop robust sustainability strategies and make data-driven decisions that efficiently reduce their environmental impact.
Image source: Carbon Tunnel Vision based on graphic by Jan Konietzko
Root’s approach to environmental sustainability
At Root, we understand the importance of taking a holistic approach to sustainability. That’s why our LCAs are comprehensive, evaluating a broad range of environmental factors, which are grouped into six key impact categories.
Below are more details about each impact category:
| Impact Category | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Climate change | Measures the greenhouse gases emitted by your company’s activities and their contribution to global warming. |
| Ecosystem quality | Assesses the impact of industrial activities on biodiversity, habitat integrity and the overall health of ecosystems. |
| Material resources | Evaluates the consumption and depletion of natural resources, including minerals and fossil fuels, throughout a product’s life cycle. |
| Pollution | Analyses the release of contaminants into the environment, affecting the quality of air, water and soil. |
| Toxicity | Examines the release of harmful substances into the environment and their potential effects on human health and ecosystems. |
| Water use | Measures freshwater consumption and its effects on water availability and aquatic ecosystems. |
Root’s LCAs create complete product footprints. This enables businesses to effectively balance trade-offs between environmental factors and make informed, data-driven decisions.
Below is an overview of how Root measures and reduces companies like yours environmental impact in three simple steps:
Retrieve data
First, upload your data onto Root’s platform. We need information about your purchase and sales orders to map your supply chain and details about your products, suppliers and transport routes.
Organise insights
Once your data is uploaded, Root’s platform will generate thousands of product life cycles at once, converting your product data into impact data. Our unique algorithms and LCA databases will give you a comprehensive view of all your products’ environmental impact.
Optimise impact
Now that you have the data, it’s time to take action. Our dashboards identify which materials or processes contribute the most to your environmental impact.
Additionally, you can use Root’s scenario builder to test ways to reduce your environmental footprint. With detailed product-level insights, you can implement changes to effectively reduce your environmental impact.
Are you interested to learn more about how Root can help you measure and reduce your environmental footprint? Book a demo with our experts here.
How we can help
At Root, we aim to redefine the norm by making product footprints universal. Our platform conducts automated LCAs for entire product portfolios – helping businesses report effectively on regulations, avoid greenwashing and become industry leaders in sustainability.
Root creates comprehensive LCAs that help businesses accurately measure and reduce their environmental impact.
Interested to learn more? Get in touch with our team to discover how Root can help you measure and reduce carbon emissions and drive sustainable growth.
